Improving collaboration of care is possible and an essential aspect of substance use disorder treatment that involves multiple healthcare professionals and organizations working together to provide the best possible care for individuals who are suffering. This approach recognizes that addiction is a complex disorder that requires a multifaceted approach to treatment and involves various aspects of an individual’s physical, mental, and social well-being. In this post, we will explore the importance of collaboration in SUD (Substance Use Disorder) treatment, provide some statistics on the prevalence of substance abuse, and examine a few case studies to illustrate the benefits of this approach.
According to the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), approximately 21 million people in the United States suffer from substance use disorders. Substance abuse is a significant public health problem that can have profound consequences for individuals, families, and communities. The negative effects of substance abuse can include physical and mental health problems, financial instability, and social isolation.
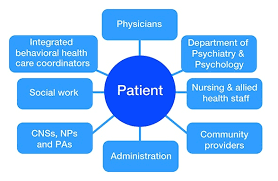
Collaboration of care in SUD treatment involves multiple providers working together to address all aspects of an individual’s well-being. This may include medical professionals, mental health professionals, social workers, and addiction specialists. It may also involve coordination with other organizations.
While collaboration of care does provide many benefits, it requires enhanced communication between providers. Electronic health records software can bridge the gap. With internal messaging systems, users can share information on patients’ treatment journey status and progression in recovery, as well as coordinate administrative tasks such as verification of benefits and prior authorizations required. Additionally, secure and efficient exchange of information such as medications and laboratory results can improve patient safety.
Coordinating efforts between providers can also help to improve the effectiveness of care by ensuring that individuals receive the most appropriate treatment for their specific needs. This can help to reduce the risk of relapse and improve long-term recovery outcomes. One example is the use of medication-assisted treatment (MAT) in conjunction with counseling and other support services. MAT involves the use of medications, such as methadone and buprenorphine, to help individuals overcome their addiction to opioid drugs. Research has shown that MAT is highly effective in reducing opioid addiction and overdose deaths. However, MAT is most effective when it is used with counseling and other support services, such as social support and job training.
Access to patient history is another requirement for proper collaborative care. By having comprehensive information about a patient’s previous admissions, treatments, medications, and other relevant data, providers can make more informed decisions and tailor their care plans accordingly. Patient history enables professionals to identify patterns, potential risk factors, and underlying conditions that may impact their current health status. With insight into a patients’ recovery journey and diagnosis history, providers can individualize each course of treatment to further progress towards long-term recovery.
Peer support programs involve individuals in recovery, providing support and guidance to other individuals struggling with addiction. Research has shown that peer support programs can be highly effective in helping individuals maintain long-term recovery. It creates a sense of belonging and reduces isolation by connecting individuals with others who have shared experiences and challenges. Through empathy, understanding, and shared wisdom, peers provide a unique form of support that professionals may not fully comprehend. Peer support also promotes empowerment and self-determination, encouraging individuals to take an active role in their recovery journey. It enhances social skills, communication, and coping mechanisms, allowing individuals to develop healthier relationships and improve their overall well-being.
To summarize, collaboration of care is an essential aspect of substance use disorder and other behavioral health treatment. Viewing a patient as a whole person rather than a particular diagnosis enables providers to solve issues at the root cause. If your treatment organization would like to learn more about how to improve provider collaboration for higher quality care, schedule a demo at www.medicalmime.com/main/contact.
